Hydrogen Bunkering
Hydrogen bunkering methods for ships: fixed installation, truck-to-ship, ship-to-ship & container swap. Transfer rates, costs & infrastructure guide.
⛽
Hydrogen Bunkering Methods
Four approaches to refueling hydrogen-powered vessels—from fixed installations to innovative container swapping systems
Maritime hydrogen bunkering remains in its infancy, with infrastructure developing alongside the first generation of hydrogen-powered vessels. Unlike conventional marine fuels with established global supply chains, hydrogen bunkering requires purpose-built solutions tailored to the fuel’s unique physical properties—whether stored as compressed gas at 350–700 bar or as cryogenic liquid at -253°C.
Four distinct bunkering approaches have emerged, each offering different trade-offs between infrastructure investment, operational flexibility, and transfer efficiency. The optimal choice depends on vessel type, route patterns, and the maturity of hydrogen supply at specific ports.
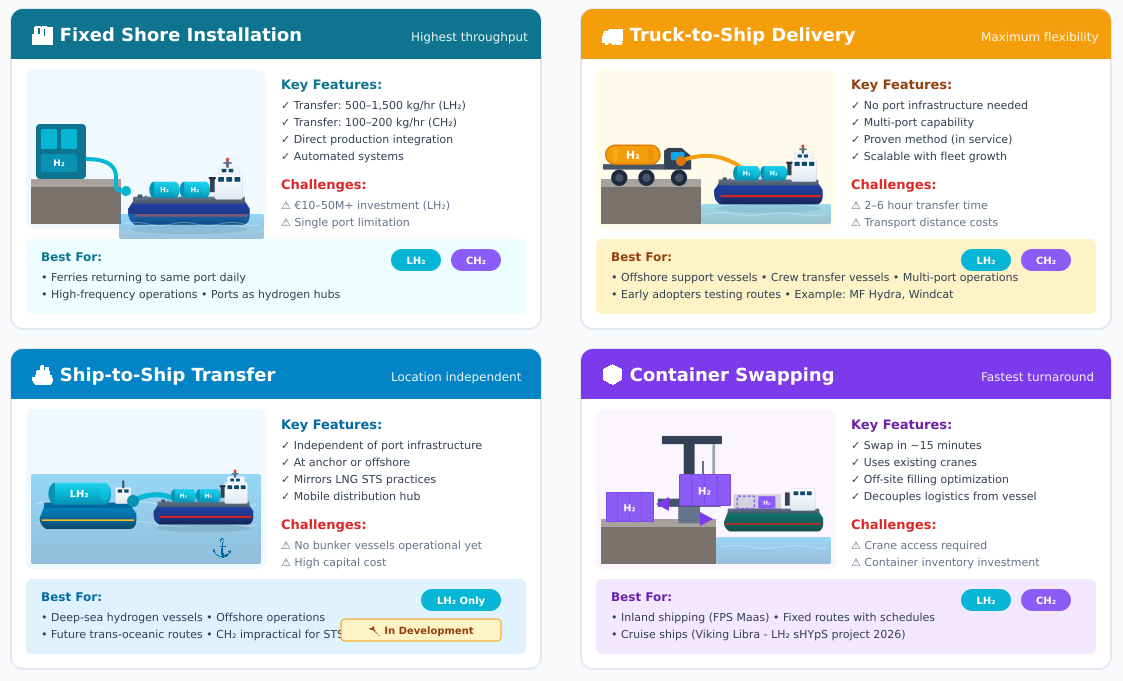 Four distinct approaches to maritime hydrogen bunkering serve different operational requirements and infrastructure availability.
Four distinct approaches to maritime hydrogen bunkering serve different operational requirements and infrastructure availability.
Bunkering Methods at a Glance
| Method | H₂ Form | Location Flexibility | Transfer Speed | Infrastructure Cost | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Shore Installation | CH₂ LH₂ | Low—single port | Fastest | High | Ferries, regular routes |
| Truck-to-Ship | CH₂ LH₂ | High—any accessible quay | Moderate | Low | Multi-port operations, early adopters |
| Ship-to-Ship | LH₂ | Very high—at anchor/offshore | Moderate–Fast | Medium–High | Deep-sea vessels, offshore operations |
| Container Swapping | CH₂ LH₂ | Medium—crane-equipped ports | Very fast (swap only) | Medium | Inland shipping, fixed routes |
Note: Transfer speeds and costs vary significantly based on specific equipment, pressure differentials, and local conditions. Values shown are general guidance.
Explore Each Method
[ 🏭 Fixed Shore Installation Permanent quayside bunkering stations offering highest throughput for vessels on regular routes.
- Fastest transfer rates
- Direct integration with H₂ production
- High infrastructure investment
Learn More → ](bunkering-fixed-installation.html) [ 🚛 Truck-to-Ship Delivery Mobile bunkering via tube trailers or cryogenic tankers—flexibility without port infrastructure.
- Minimal port investment
- Multi-port capability
- Proven by early adopters
Learn More → ](bunkering-truck-to-ship) [ 🚢 Ship-to-Ship Transfer Bunker vessel delivers LH₂ at anchor or offshore—essential for deep-sea operations.
- Location independent
- Primarily liquid hydrogen
- Future development focus
Learn More → ](bunkering-ship-to-ship.html) [ 📦 Container Swapping Exchange depleted containers for pre-filled units—minutes instead of hours.
- Fastest turnaround
- Leverages existing cranes
- LH₂ version under development
Learn More → ](bunkering-container-swap.html)
Safety & Regulatory Framework
Hydrogen bunkering safety builds on decades of industrial hydrogen handling experience, adapted for the marine environment. International standards are evolving rapidly as operational experience accumulates.
Key Safety Considerations
Universal Requirements
- Hazardous area classification and ventilation
- Gas detection and emergency shutdown systems
- Grounding and bonding for static discharge
- Exclusion zones during transfer operations
- Trained personnel with hydrogen-specific certification
Key Standards: IGF Code (IMO), ISO 20519 (ship bunkering), SGMF guidelines, and classification society rules from DNV, Lloyd’s Register, and others provide the regulatory framework for hydrogen bunkering operations.
Current & Planned Bunkering Infrastructure
🗺️
Interactive Map: Hydrogen Bunkering Locations
View operational and planned bunkering facilities across Europe
🇳🇴 Norway 🇳🇱 Netherlands 🇩🇪 Germany 🇧🇪 Belgium 🇫🇷 France 🇬🇧 United Kingdom
See also: H₂ Liquefaction Facilities Map for upstream supply infrastructure critical to LH₂ bunkering availability.
Related H₂ Supply Resources
H₂ Production Methods → H₂ Liquefaction Facilities → H₂ Price & Economics → Ship Projects Database →